TILLING (targeting Induced Local Lesions In Genome) is an efficient tool in detecting the mutation of target DNA fragment in reverse genetics. Rice is a model monocotyledon plant and an important crop plant. The establishment of TILLING in rice can promote analysis of gene function and uses of mutant in rice breeding. Several TILLING platforms have been established, however, the efficiency in obtaining mutations of target gene is low. To meet the allelic variations needs of researchers, we established a more efficient mutation screening TILLING platform.
The EMS mutant population used in the our TILLING platform contains 6,000 M2 plants, and possesses high frequency of the nucleic acid changes (1.5-kb per change). A DNA pool of the M2 population was made according to our 2D-Merge Pooling method (1:8 pooling). The pooling DNA was then used as the template to amplify the DNA fragment of interest with high fidelity DNA polymerase. The PCR product was firstly digested by optimized CELI to cleavage the nucleic acid mismatch, then analyzed by automatic electrophoresis and imaging system. The work flow of TILLING is presented in Figure 1. Until now, we have provided services to almost 30 research groups.
Figure 1. The workflow of rice TILLING platform
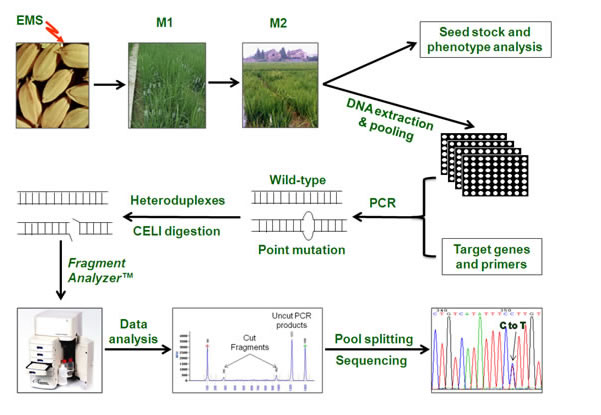
1.The seeds of ZH11 were mutagenized by EMS to produce M0 seeds
2.Plant M0 seeds to produce M1 mutagenesis population
3.Collect and plant M2 seeds which are from the main tillers of M1 plants to produce M2 mutagenesis population
4.Use the leaves of the individual M2 plant to perform the genomic DNA extracting, homogenization of the concentration and making DNA pool
5.Collect the M3 seeds of individual M2 plant to perform the genomic DNA extracting
6.Identified the target genes and design specific primers of the genes
7.PCR
8.The PCR product was treated by heat denaturation and renaturation slowly to form heteroduplex-double strands which was then digested by CEL 1
9.Isolated the CEL 1 digested product by Fragment Analyzer™ automatic capillary column electrophoresis system
10.To obtain the samples with point mutation which are from the DNA mixed-pool by data analyzing
11. Separate the samples with point mutation which are from the DNA mixed-pool to perform sequencing and identify the point mutation |